Release lifecycle management with Helm
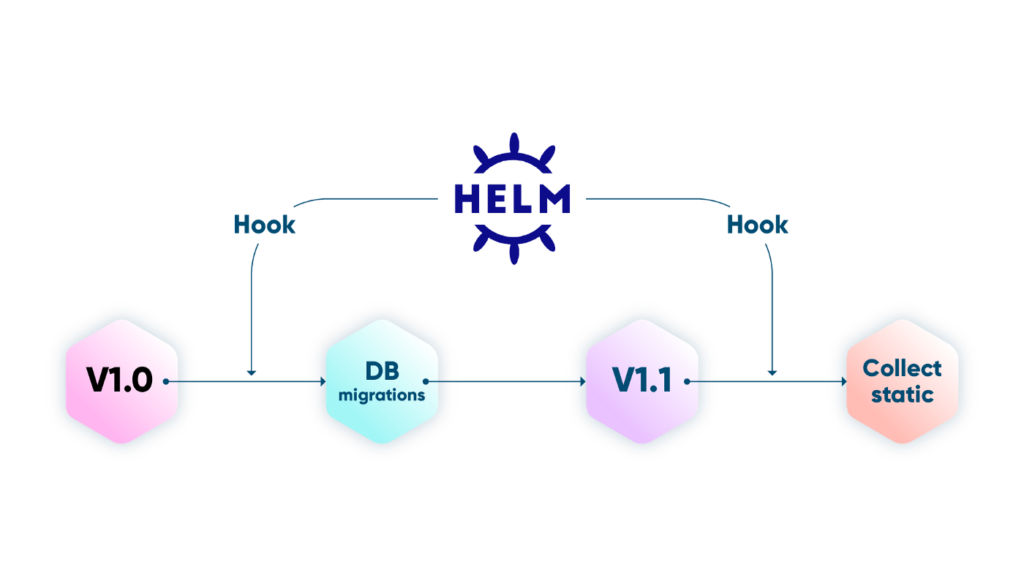
Have helm take care of the entire release lifecycle of our application.
When releasing a new version to production, not always but mostly, before being able to start the containers of our new version it is necessary to carry out some preliminary tasks. Not only prior to deployment, sometimes after the version changes it is necessary to perform some additional tasks to ensure the application works as expected. This is why Helm created charts hooks.
Hooks allow you, the chart developer, an opportunity to perform operations at strategic points in a release lifecycle. Hooks work like regular templates, but they have special annotations that cause Helm to utilize them differently. The available annotations are: (ref: https://helm.sh/docs/topics/charts_hooks/):
pre-installExecutes after templates are rendered, but before any resources are created in Kubernetespost-installExecutes after all resources are loaded into Kubernetespre-deleteExecutes on a deletion request before any resources are deleted from Kubernetespost-deleteExecutes on a deletion request after all of the release’s resources have been deletedpre-upgradeExecutes on an upgrade request after templates are rendered, but before any resources are updatedpost-upgradeExecutes on an upgrade request after all resources have been upgradedpre-rollbackExecutes on a rollback request after templates are rendered, but before any resources are rolled backpost-rollbackExecutes on a rollback request after all resources have been modifiedtestExecutes when the Helm test subcommand is invoked
Writing a Hook
Hooks are just Kubernetes manifest files with special annotations in the metadata section. Because they are template files, you can use all of the normal template features, including reading .Values, .Release, and .Template.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/version: {{ .Chart.AppVersion }}
helm.sh/chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
annotations:
# This is what defines this resource as a hook. Without this
# line, the job is considered part of the release.
"helm.sh/hook": pre-upgrade,pre-install
"helm.sh/hook-weight": "1"
"helm.sh/hook-delete-policy": before-hook-creation
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: {{ .Release.Service | quote }}
app.kubernetes.io/instance: {{ .Release.Name | quote }}
helm.sh/chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version }}"
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: db-migrations
image: "myapp:v1.1"
command: ["run","db-migrations"]
What makes this template a hook is the annotation:
annotations:
"helm.sh/hook": pre-upgrade,pre-installThis will create a db-migrations job BEFORE upgrading or installing the release for this chart. As soons as the job finishes it will rollout the new version for our application.
Hook weight
It is possible to define a weight for a hook which will help build a deterministic executing order. Weights are defined using the following annotation:
annotations:
"helm.sh/hook-weight": "5" If no weight is set, helm will apply the default value of 0.

Hook deletion policies
It is possible to define policies that determine when to delete corresponding hook resources. Hook deletion policies are defined using the following annotation:
annotations:
"helm.sh/hook-delete-policy": before-hook-creation,hook-succeededThe available annotations are:
before-hook-creation:Delete the previous resource before a new hook is launched (default)hook-succeeded:Delete the resource after the hook is successfully executedhook-failed:Delete the resource if the hook failed during execution
If no hook deletion policy annotation is specified, the before-hook-creation behavior applies by default.
Conclusion
Hooks allow chart developers to control the release lifecycle of their applications. This way they can ensure that all the necessary steps for the release to be successful can be implemented in the right order.
Questions?
Please feel free to join us on Craftech’s community Slack and ask any questions.